
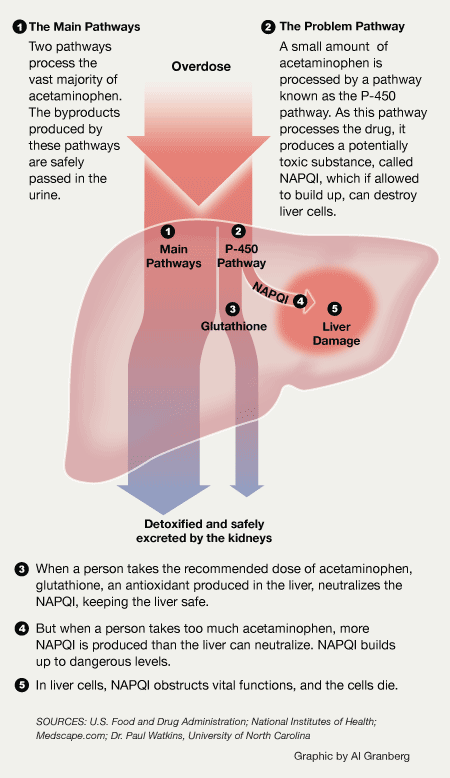
It is possible for patients to present in liver failure days after ingestion with undetectable serum APAP concentrations. Peak serum transaminase activities usually occur 48-96h after acute ingestion. However, histories concerning the time of ingestion and the amount of drug ingested are usually unreliable. A nomogram of serum APAP concentration vs hours post-ingestion can assist in determining risk of liver injury and need for treatment.

For an acute overdose, most adults must ingest about 12g or more acetaminophen (APAP) before risk of serious hepatotoxicity is of concern. A review of the typical clinical course, diagnosis and treatment of acetaminophen toxicity is provided.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
